In this series, I’m discussing how ideas from calculus and precalculus (with a touch of differential equations) can predict the precession in Mercury’s orbit and thus confirm Einstein’s theory of general relativity. The origins of this series came from a class project that I assigned to my Differential Equations students maybe 20 years ago.
We have shown that the motion of a planet around the Sun, expressed in polar coordinates  with the Sun at the origin, under general relativity follows the initial-value problem
with the Sun at the origin, under general relativity follows the initial-value problem
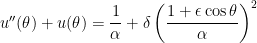 ,
,
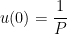 ,
,
 ,
,
where 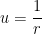 ,
, 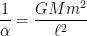 ,
, 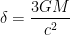 ,
,  is the gravitational constant of the universe,
is the gravitational constant of the universe, 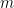 is the mass of the planet,
is the mass of the planet,  is the mass of the Sun,
is the mass of the Sun, 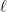 is the constant angular momentum of the planet,
is the constant angular momentum of the planet,  is the speed of light, and
is the speed of light, and 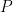 is the smallest distance of the planet from the Sun during its orbit (i.e., at perihelion).
is the smallest distance of the planet from the Sun during its orbit (i.e., at perihelion).
We now take the perspective of a student who is taking a first-semester course in differential equations. There are two standard techniques for solving a second-order non-homogeneous differential equations with constant coefficients. One of these is the method of constant coefficients. To use this technique, we first expand the right-hand side of the differential equation and then apply a power-reduction trigonometric identity:
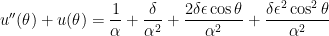
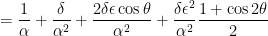
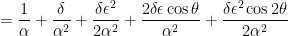
This is now in the form for using the method of undetermined coefficients. However, in this series, I’d like to take some time to explain why this technique actually works. To begin, we look at a simplified differential equation using only the first three terms on the right-hand side:
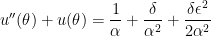 .
.
Let 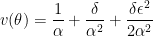 . Since
. Since  is a constant, this function satisfies the simple differential equation
is a constant, this function satisfies the simple differential equation 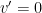 . Since
. Since 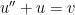 , we can substitute:
, we can substitute:
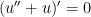
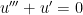
(We could have more easily said, “Take the derivative of both sides,” but we’ll be using a more complicated form of this technique in future posts.) The characteristic equation of this differential equation is 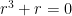 . Factoring, we obtain
. Factoring, we obtain 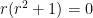 , so that the three roots are
, so that the three roots are 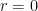 and
and 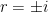 . Therefore, the general solution of this differential equation is
. Therefore, the general solution of this differential equation is
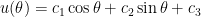 .
.
Notice that this matches the outcome of blindly using the method of undetermined coefficients without conceptually understanding why this technique works.
The constants  and
and  are determined by the initial conditions. To find
are determined by the initial conditions. To find 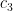 , we observe
, we observe

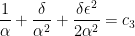 .
.
Therefore, the general solution of this simplified differential equation is
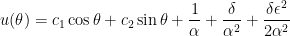 .
.
Furthermore, setting 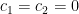 , we see that
, we see that

is a particular solution to the differential equation
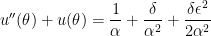 .
.
In the next couple of posts, we find the particular solutions associated with the other terms on the right-hand side.
and
are chosen at random (uniformly) from the interior of a unit circle. What is the probability that the circle whose diameter is segment
lies entirely in the interior of the unit circle?
be the interior of the circle centered at the origin
with radius
. Also, let
denote the circle with diameter
, and let
be the distance of
from the origin.
.
, I will integrate over this conditional probability:
,
is the cumulative distribution function of
. For
,
.
.
. Then the endpoints
and
become
and
. Also,
. Therefore,
,





